UNCTAD has worked to shape the global understanding of the creative economy since 2004 on a mission to promote development through creativity.
UNCTAD’s work has elevated the ‘creative economy’ on the world economic and development agenda. The programme’s core focus is on trade in creative goods and services that underpin the activity of the creative industries.
The UNCTAD Creative Economy Programme generates economic information through a trade lens, to understand past trends and project into the future and to promote data-led understanding of trade in creative goods and services, intellectual property, ideas and imagination.
The programme contributes to the research and analysis published by The United Nations Economist Network.
What is the creative economy?
The creative economy has no single definition. It is an evolving concept which builds on the interplay between human creativity and ideas and intellectual property, knowledge and technology. Essentially it is the knowledge-based economic activities upon which the ‘creative industries’ are based.
The creative industries – which include advertising, architecture, arts and crafts, design, fashion, film, video, photography, music, performing arts, publishing, research & development, software, computer games, electronic publishing, and TV/radio – are the lifeblood of the creative economy. They are also considered an important source of commercial and cultural value.
The creative economy is the sum of all the parts of the creative industries, including trade, labour and production. Today, the creative industries are among the most dynamic sectors in the world economy providing new opportunities for developing countries to leapfrog into emerging high-growth areas of the world economy.
Creative Economy Mandates
UNCTAD’s mandate to conduct research and policy analysis, consensus building, and technical cooperation remains as valid and important today as it was more than a decade ago when in 2004 the UNCTAD Secretary-General established the Creative Economy Programme.
After being incorporated into the mandate, the Creative Economy Programme was reconfirmed and expanded at UNCTAD Ministerial Conferences between 2004 and 2016.
In 2023, the United Nations General Assembly at its Seventy-eighth session adopted Resolution 78/133: Promoting creative economy for sustainable development.
Programme Mandates
General Assembly (2023)
Resolution 78/133: Promoting creative economy for sustainable development
A/RES/78/133 - 21 Dec 2023
English | Français | Español | العربية | 简体中文 | Русский | DeutschUNCTAD XV, Bridgetown Covenant (2021)
The Bridgetown Covenant, Fifteenth session of the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development,5 November 2021.
The creative economy has become an important contributor to economic growth and serves as a new prospect for developing countries to diversify their economies and leapfrog into new, high-growth sectors of the world economy towards achieving the Sustainable Development Goals. It is thus important to create an enabling environment for the promotion of the creative economy, among others, by encouraging creativity, innovation and entrepreneurship, supporting the development of cultural institutions and cultural industries, providing technical and vocational training for culture professionals and increasing employment opportunities in the cultural and creative sector.
(Bridgetown Covenant, para. 54)
UNCTAD should:
Continue the work on analysing the creative industries and providing insight into the global creative economy through the UNCTAD creative economy programme and creative economy network that can support countries to take advantage of the potential offered in this field.
(Bridgetown Covenant, para. 127 (ee).
UNCTAD XV, Bridgetown Accord (2021)
The Bridgetown Accord (TD/540), Creative Economy and Trade Digitalization Forum, Fifteenth session of the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development, 5 November 2021.
Among the many recommendations, the Accord calls on UNCTAD to place greater emphasis on the social and developmental benefits of the creative and technological sectors as well as Commit and contribute to the centring of cultural and creative industries as a driver of trade, development and national and regional systems of innovation.
UN 2021 International Year of the Creative Economy for Sustainable Development (2019)
United Nations resolution declaring 2021 the “International Year of Creative Economy for Sustainable Development”
In December 2019, the United Nations General Assembly in New York adopted resolution, 74/198 (2019), by consensus. This was a landmark achievement for the creative industries, recognizing them as crucial sectors for the attainment of the 2030 agenda, emphasizing the role of international trade in creative goods and services and its contribution to the global economy, and requested UNCTAD to monitor and write the report on the resolution's implementation on behalf of the UN Secretary-General with support from UNESCO and other agencies.
UNCTAD XIV, Nairobi Maafikiano (2016)
In line with UNCTAD’s Nairobi Maafikiano mandate (TD/519), the Creative Economy Programme will contribute to a more balanced and inclusive trade in new dynamic sectors and will take a multi-stakeholder consultation approach. National stakeholders - from government ministries and specialized agencies, the private sector and civil society, including creative industries associations, businesses, academia and workers - are key players in this process. Through national studies, surveys, databases and deliberations of national workshops, stakeholders will examine different policy domains - including the interface between competition and industrial policies, consumer protection, fiscal policy, trade policy, tariff and non-tariff measures, intellectual property regimes, education policy, financial schemes, institutions and international cooperation - to promote promising creative industries sectors.
UNCTAD XII, Accra (2008)
The panel recognized that UNCTAD’s work in the area of the creative economy and the creative industries should be pursued and enhanced. It was felt that UNCTAD should continue to fulfil its mandates and assist Governments on issues related to the development dimension of the creative economy, in line with the three pillars of UNCTAD´s work: (a) consensus-building, by providing a platform for intergovernmental debates; (b) policy-oriented analysis, by identifying key issues underlying the creative economy and the dynamics of creative industries in world markets; and (c) technical cooperation, by assisting developing countries to enhance their creative economies for trade and development gains.
(Secretary-General´s high-level panel on the creative economy and industries for development)
UNCTAD XI, São Paulo (2004)
The international community should support national efforts of developing countries to increase their participation in and benefit from dynamic sectors and to foster, protect and promote their creative industries.
(São Paulo Consensus, para.91)
Creative industries can help foster positive externalities while preserving and promoting cultural heritages and diversity. Enhancing developing countries´ participation in and benefit from new and dynamic growth opportunities in world trade is important in realizing development gains from international trade and trade negotiations and represents a positive-sum game for developed and developing countries.
(São Paulo Consensus, para. 65)
In focus
The Creative Economy Outlook provides insights into the creative economy and international trade in creative goods and services.
The report covers recent trends and developments in creative industries and international trade of creative products.
The Creative Economy Outlook 2024 focuses on the impact of digitalization and artificial intelligence on the creative economy, competition challenges, and sustainability efforts.
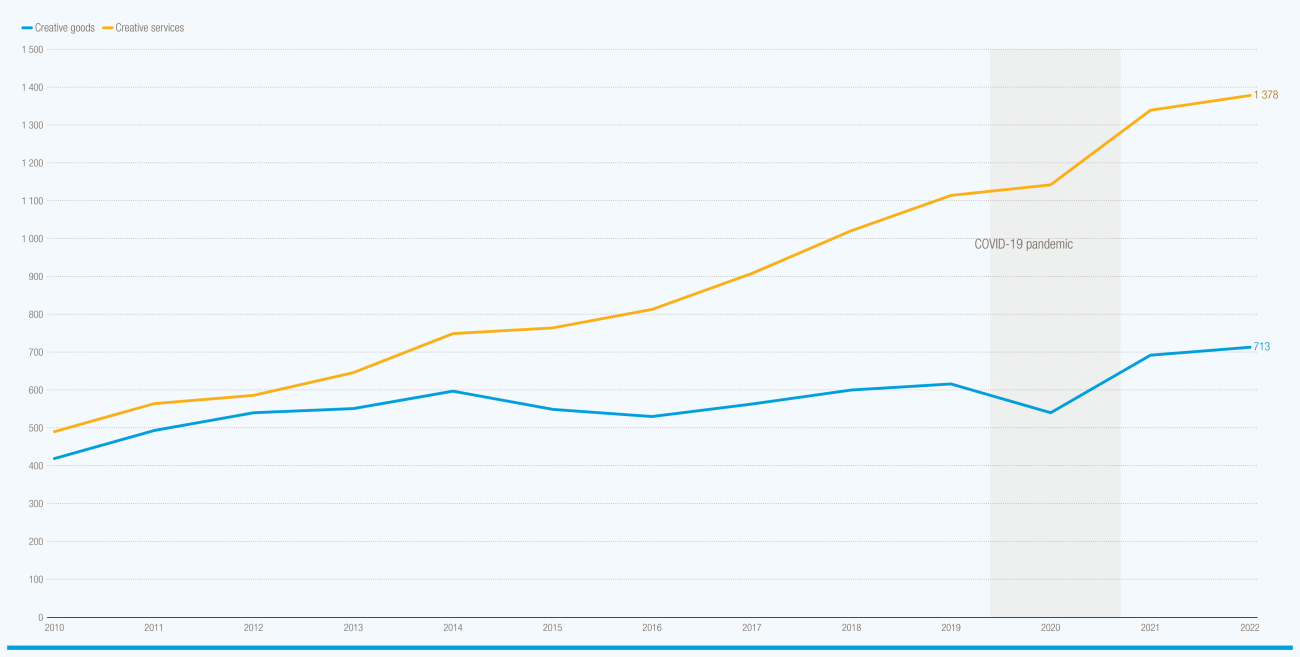
The 2024 report underscores the pivotal role that creative industries play in trade and economic growth. UNCTAD’s global survey reveals the varied economic contributions of the creative economy across different countries, ranging from 0.5% to 7.3% of GDP and employing between 0.5% to 12.5% of the workforce.
News
Publications
Podcast
Bright ideas: How creativity can power economies and development
Creative Economy Network
Events & meetings
23 – 25 April 2025
Workshop on culture and creative economy foresight
20 – 21 June 2024
Workshop on harnessing the creative economy for Ethiopia's sustainable development
15 September 2023
WTO Public Forum 2023 - Harnessing the digital creative economy in small economies: Creating pathways towards services-led diversification
13 September 2023
Launch of report on mapping the cultural and creative industries in Angola
11 – 12 September 2023
Workshop on Intellectual Property Rights for cultural and creative industries stakeholders in Angola
Statistics
UNCTAD compiles and publishes data about international trade in creative goods and services, which can be accessed on the UNCTADstat Data centre.
The methodology for this data is detailed in the report titled Advancing the measurement of the creative economy: A revised framework for creative industries and trade, as well as in the metadata.